|

|

|
Constant Voltage
Charging
|
Constant-voltage (often called constant-potential) chargers
maintain nearly the same voltage input to the battery throughout the
charging process, regardless of the battery's state of charge.
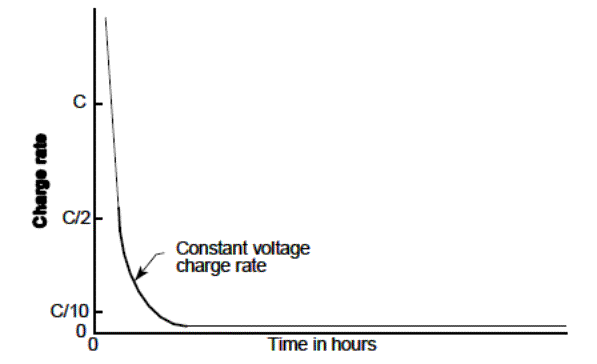
Constant-voltage chargers provide a high initial current to the battery
because of the greater potential difference between the battery and
charger. A constant-voltage charger may return as much as 70% of the
previous discharge in the first 30 minutes. This proves useful in many
battery applications involving multiple discharge scenarios. As the battery
charges its voltage increases quickly. This reduces the potential that has
been driving the current, with a corresponding rapid decrease in charge
current as depicted in the illustration below. As a result, even though the
battery reaches partial charge quickly, obtaining a full charge requires
prolonged charging.
Given this behavior, constant-voltage chargers are frequently found
in applications that normally allow extended charging periods to attain
full charge. Constant-voltage chargers should not be used where there is
frequent cycling of the battery. Repeated discharges without returning the
cell to its full charge will eventually decrease the battery capacity and
may damage individual cells.
Constant-voltage chargers are most often used in two very different
modes: as a fast charger to restore a high percentage of charge in a short
time or as a float charger to minimize the effects of overcharge on
batteries having infrequent discharges.
 Back to top Back to top
|
Have questions? Contact TECH SUPPORT:
Corporate
|
About Us | Site Map | Services | Clients | Global Presence
| Email: Parts &
Service | Battery Care
Privacy |
Terms of Use |
Ethics |
Legal

Powered by: Sun Microsystems
© Copyright GB Industrial Battery - All rights reserved.
Last Updated: Monday, December 03, 2007 - 6:07 AM Eastern Time.
 
|